

When a word such as “over” or “up” is modifying a verb, it’s acting like an adverb. Sometimes, words you might think of as prepositions act like adverbs. Thankfully, Hugh couldn’t find the anchovies.opens in a new windowAdverbs often end with “-ly,” but not always. AdverbsĪdverbs can modify verbs (or verb phrases), adjectives (or adjective phrases), other adverbs (or adverb phrases), and whole sentences. Opens in a new windowSometimes you need commas between adjectives, and sometimes you don’t. Nouns can also function as adjectives, and when they do, they are called opens in a new windowattributive nouns: Some systems call words such as “a” and “the” and “my” and “his” adjectives. This piece about opens in a new window“bad” and “badly” explains more about linking verbs. Aardvark was the best fishing buddy today.Linking verbs connect a subject to a descriptor. They can convey a sense of time, possibility, ability, and so on: Helping verbs (aka opens in a new windowauxiliary verbs) add meaning to the main verb. Verbs can describe actions, help other verbs, and link a subject to descriptors. Nouns can also be categories as opens in a new windowconcrete, abstract, collective, and compound. The first letter of a proper noun is capitalized.Ĭommon nouns are the generic names of people, places, things, and concepts. Proper nouns are the given names of people, places, and things. Nouns are names of people, places, things, and concepts. Opens in a new windowSome nouns need an article before them, and some don’t.
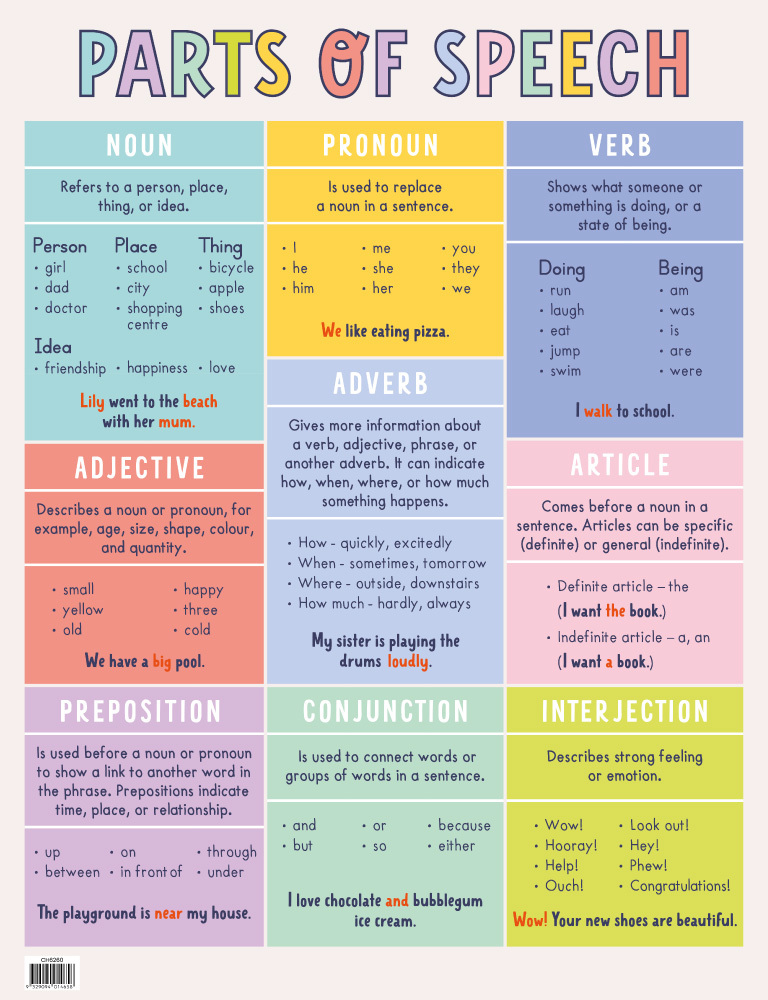
Remembering three things is much easier than remembering eight.Some other grammar classification systems group articles with adjectives or call them determiners. The parts of speech really boil down to nouns, verbs, and modifiers. Students will probably say that it is a joining word. Point at those two words but don't write down "Preposition."Īsk what a conjunction is. Say that it is a word that creates a phrase that functions as an adjective or adverb. They are so unimportant, you won't even write the word down.Īsk what a preposition is. How nice." Point out that the two things you just said are interjections. Write "Adverb" to the right of "Verb."Īsk what an interjection is. Students will say that it modifies a verb (or adjective or other adverb). Write "Adjective" to the left of "Noun."Īsk what an adverb is. Students will say that it modifies a noun. Point to "Noun" but do not write "Pronoun."Īsk what an adjective is. Students will probably be able to say that it takes the place of a noun (or other pronoun). Subject and predicate."Īsk what a pronoun is. Then ask "What is a verb?" Most students will be able to say that it is an action or state of being.ĭraw a line to connect the noun to the verb. To the right of it, write " Verb" and circle it. Then ask, "What is a noun?" Most students can recite that it is a person, place, or thing (or idea). On the board, write " Noun" and circle it. Help simplify the parts of speech graphically. They have a right to: Eight of anything is a lot to keep track of. Read off the eight parts of speech to your students.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
